Jal Jeevan Mission: Reshaping Rural India - A Water Access Odyssey
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Introduction:
The Jal Jeevan Mission (JJM) is a transformative initiative undertaken by the Government of India to address the critical issue of water scarcity and inadequate water supply in rural areas. This report discusses the key aspects of the Jal Jeevan Mission, its objectives, achievements, and the innovative approach it takes to ensure water security for all.
Progress and Objectives:
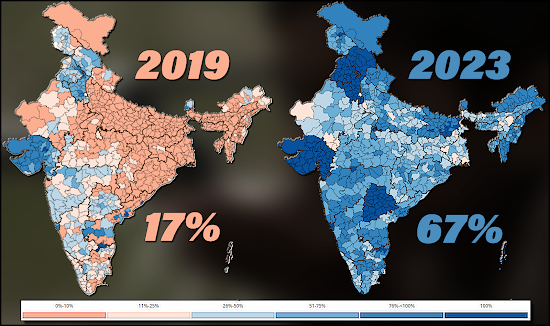
In 2019, only 17% of households in rural India had water connections.
By August 2023, this number had risen significantly to 67.25%.
The primary goal of JJM is to provide tap connections to 100% of rural households in India, ensuring access to a daily supply of 55 liters of water per person till year 2024.
Demand-Driven Model vs. Supply-Driven Model:
Earlier attempts by previous administrations, such as the UPA, aimed at similar schemes but faced challenges.
JJM adopts a demand-driven model where resources are allocated based on specific requests from regions, unlike the supply-driven approach.
The supply-driven model led to resource allocation without analyzing demand, while JJM emphasizes addressing where water is needed the most.
Implementation Structure:
Water Supply Committees called 'Pani Samiti' were established in each village to oversee the mission's implementation.
The committee, led by the village sarpanch, is responsible for creating a village action plan and water supply infrastructure.
A public health engineer provides the committee with three action plan options, including water tap connections, distribution facilities, and water treatment plants.
Ensuring Quality and Sustainability:
Members of various local groups, including Anganwadi workers, ASHA workers, self-help groups, PRI members, and school teachers, are trained to test water quality using Field Test Kits.
Maintenance and operation are funded by the Pani Samiti, enabling timely repairs and upkeep of the water supply infrastructure.
Learning from Past Mistakes:
Under the previous approach, state and union territories struggled with annual action plan creation and fund management.
JJM's performance-based fund allocation ensures efficient utilization of resources and focuses on results at the district level.
Addressing Vulnerable Sections:
Priority is given to poor, backward classes, and areas affected by contaminated water, along with villages under specialized government schemes.
Women, who were disproportionately affected by the water crisis, are included in decision-making through the rule that half of Pani Samiti members must be women.
Groundwater Challenges and Recommendations:
Earlier reliance on handpumps led to contamination of groundwater with heavy metals, causing waterborne diseases.
Experts recommend water conservation through rainwater harvesting and recycling to reduce the heavy dependence on groundwater.
Impact and Way Forward:
Despite challenges related to water safety and information dissemination, JJM has made a significant positive impact on people's lives.
The mission has the potential to address water-related health issues, reduce child mortality due to diseases like diarrhea, and improve overall living conditions.
Conclusion:
The Jal Jeevan Mission is a commendable endeavor that focuses on providing rural households with access to clean and safe drinking water. By adopting a demand-driven approach, involving local communities, addressing gender disparities, and emphasizing sustainable practices, JJM is working towards transforming water accessibility and quality in rural India. While challenges remain, the progress and positive outcomes achieved by the mission underline its importance in improving the lives of millions of people across the country.
Reference:
Jal Jeevan Mission about page
Jal Jeevan Mission progress report
Article inspiration
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Comments


Useful information
ReplyDelete